38 risk of zero coupon bonds
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Advantages, Risks A zero-coupon bond is a discounted investment that can help you save for a specific future goal. Tara Mastroeni. Nov 25, 2020, 10:09 AM. Save Article Icon. A bookmark. Facebook Icon. The letter F ... Zero-Coupon Bonds : What is Zero Coupon Bond? - Groww No reinvestment risk: Other coupon bonds don't allow investors to a bond's cash flow at the same rate as the investment's required rate of returns. But the Zero Coupon bonds remove the reinvestment risk. Zero Coupon bonds do not allow any periodic coupon payments and thus a fixed interest on Zero Coupon bonds is assured.
Pros and Cons of Zero-Coupon Bonds | Kiplinger With retirement years away for you and today's low interest rates, we'd advise against buying zeros. These bonds don't make regular interest payments. Instead, they're sold at a big discount to...
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():saturation(0.2):brightness(10):contrast(5)/GettyImages-932585920-5c910a5846e0fb000172f0e8.jpg)
Risk of zero coupon bonds
corporatefinanceinstitute.com › zero-coupon-bondZero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds. Understanding Zero-Coupon Bonds As a zero-coupon bond does not pay periodic coupons, the bond trades at a discount to its face value. Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds 31.01.2022 · Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds have a poor risk-return profile when held alone. Long-dated zero-coupon Treasury bonds are more volatile than the stock market, but they offer the lower long-run ... The Pros and Cons of Zero-Coupon Bonds Another problem with zero coupon bonds is that they have a higher default risk than traditional bonds. The reason behind this is that companies do not have to make regular interest payments to the investors. They just keep all of the money and do with it as they please.
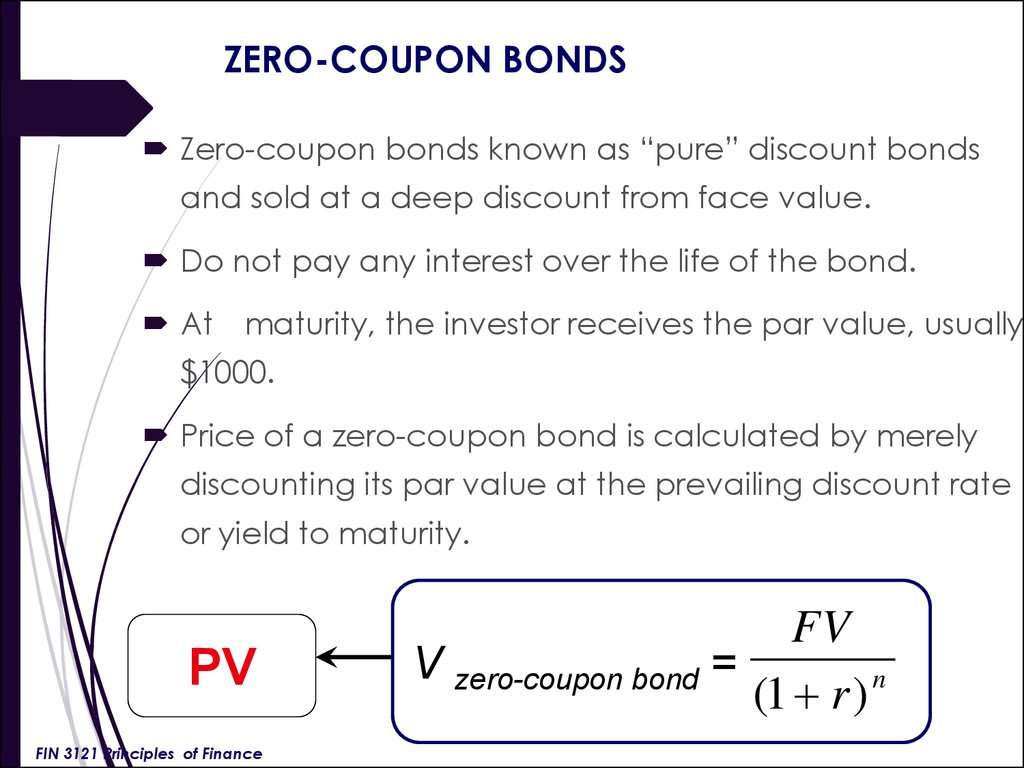
Risk of zero coupon bonds. How to Calculate a Zero Coupon Bond Price | Double Entry ... The zero coupon bond price or value is the present value of all future cash flows expected from the bond. As the bond has no interest payments, the only cash flow is the face value of the bond received at the maturity date. Zero Coupon Bond Pricing Example. Suppose for example, the business issued 3 year, zero coupon bonds with a face value of ... Is TBT Still The Way To Play Interest Rates? What The ... The PIMCO 25+ Year Zero Coupon U.S. Treasury Index ETF is a zero-coupon long bond fund. A zero-coupon bond features more duration risk since the investor does not receive dividends along the way. Zero Coupon Bond -Features, benefits, drawbacks ... Interest Rate Risk: Zero-coupon bonds that are sold before maturity are subject to interest rates risk. This is because the value of these bonds is inversely proportional to interest rates. Hence, if interest rates rise, the value of these bonds declines in the secondary market. Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One Risk of Default Corporate zero coupon bonds carry the most risk of default and pay the highest yields. Many of these have call provisions. How big of a discount will you pay? Here is an example of how zero coupon bond prices can change: For example, assume that three STRIPS are quoted in the market at a yield of 6.50%.
› terms › zZero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia Feb 26, 2022 · Zero-Coupon Bond: A zero-coupon bond is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full ... Bonds - Overview, Examples of Government and Corporate Bonds Zero-coupon bond. Zero-coupon bonds make no coupon payments but are issued at a discounted price. 6. Municipal bonds. Bonds issued by local governments or states are called municipal bonds. They come with a greater risk than federal government bonds but offer a higher yield. Examples of Government Bonds. 1. The Canadian government issues a 5% yield … Understanding Bonds: The Types & Risks of Bond Investments Because bonds tend not to move in tandem with stock investments, they help provide diversification in an investor's portfolio. They also provide investors with a steady income stream, usually at a higher rate than money market investments Footnote 1. Zero-coupon bonds and Treasury bills are exceptions: The interest income is deducted from their purchase price and … › article › understanding-bondsUnderstanding Bonds: The Types & Risks of Bond Investments Zero-coupon bonds and Treasury bills are exceptions: The interest income is deducted from their purchase price and the investor then receives the full face value of the bond at maturity. All bonds carry some degree of "credit risk," or the risk that the bond issuer may default on one or more payments before the bond reaches maturity.
courses.lumenlearning.com › chapter › types-of-bondsTypes of Bonds | Boundless Finance - Lumen Learning This method of creating zero coupon bonds is known as stripping, and the contracts are known as strip bonds. “STRIPS” stands for Separate Trading of Registered Interest and Principal Securities. Zero coupon bonds may be long- or short-term investments. Long-term zero coupon maturity dates typically start at 10 to 15 years. The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Like virtually all bonds, zero-coupon bonds are subject to interest-rate risk if you sell before maturity. If interest rates rise, the value of your zero-coupon bond on the secondary market will likely fall. Long-term zeros can be particularly sensitive to changes in interest rates, exposing them to what is known as duration risk. What are the advantages and disadvantages of zero-coupon bond? Answer (1 of 8): Advantages: * You can predict return * Low minimum investment * Minimal Risk * Attainment of Long Term Financial Goals * Reinvestment Risk * Can trade in secondary market. Disadvantages: * Maturity period of a zero-coupon bond is quite lengthy. * Interest rate risk * A... What is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Features ... Definition: A zero-coupon bond, as the name suggests, it is a financial instrument which does not allow a regular interest payment to the investor. Moreover, it is a bond which is issued at a meagre market price (discounted price) in comparison to its face value. And it is redeemable on or after a specified maturity date at the par value itself.
Treasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, they are issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value at the end of the tenure, which is the return on their investment. Bonds pay interest in the form of a coupon to the investors quarterly or semi-annually. T-bills have no default risk Default Risk Default risk is a form of risk that measures the likelihood of …
Investor's Guide to Zero-Coupon Municipal Bonds | Project ... Zero-coupon municipal bonds provide investors with the opportunity to lock in a specified rate of return, without having to worry about reinvestment risk or future interest rate changes. By contrast, investors in securities that pay interest semiannually may not always achieve a total realized compounded yield equal to the quoted yield to ...
How to Buy Zero Coupon Bonds | Finance - Zacks Zero coupon bonds are issued by the Treasury Department, corporations and municipalities. The bonds are considered a low-risk investment compared to stocks, commodities and derivatives. Step 1
Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia 26.02.2022 · Zero-Coupon Bond: A zero-coupon bond is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full ...
Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Excel Calculator Zero-Coupon Bond Risks Interest Rate Sensitivity One drawback to zero-coupon bonds is their pricing sensitivity based on the prevailing market interest rate conditions. Bond prices and interest rates have an "inverse" relationship with one another: Declining Interest Rates Higher Bond Prices Rising Interest Rates Lower Bond Prices
Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia Pension funds and insurance companies like to own long maturity zero coupon bonds because of their high duration. That means that the bonds' prices are particularly sensitive to changes in the interest rate, and so offset, or immunize, the interest rate risk of the firms' long-term liabilities. Taxes
Bond Yield to Maturity Calculator for Comparing Bonds Convertible bonds do offer an added opportunity to increase the return on your investment, but changing your investment from a security to a stock comes with substantially more risk. Zero Coupon Bonds. This is simply any type of bond, government or corporate, that makes no interest payments over its term. Instead, it is sold at a considerable ...
Zero Coupon Bond Definition and Example | Investing Answers What are the Risks of a Zero Coupon Bond? If you sell a zero coupon bond before the maturity date, you could face interest rate risk. Meaning, your investment may go down in value if interest rates go up. The longer the maturity date, the more risk you'll face. Verified Content You Can Trust
united states - Can zero-coupon bonds go down in price? - Personal Finance & Money Stack Exchange
Types of Bonds | Boundless Finance - Lumen Learning Zero coupon bonds may be long- or short-term investments. Long-term zero coupon maturity dates typically start at 10 to 15 years. The bonds can be held until maturity or sold on secondary bond markets. Short-term zero coupon bonds generally have maturities of less than one year and are called bills. The U.S. Treasury bill market is the most ...
Zero-Coupon Bonds: Definition, Formula, Example ... They are safe investment instruments, and have a lower element of risk involved. Long Dated zero coupon bonds are said to be the most responsive to interest rate fluctuations. Therefore, in case of longer time duration (a higher 'N'), it might prove to be profitable for the bond holder. Disadvantages of Zero-Coupon Bonds
Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula Zero-coupon bonds are the only type of fixed-income investments that are not subject to investment risk – they do not involve periodic coupon payments. Interest rate risk is the risk that an investor’s bond will decline in value due to fluctuations in the interest rate.
Should I Invest in Zero Coupon Bonds? | The Motley Fool The downsides of zero coupon bonds For some investors, being more sensitive to rate changes is a negative rather than a positive. If you don't intend to hold your bond to maturity, you have to stay...
Zero Coupon Bond - WallStreetMojo These Bonds avoid the risk of Reinvestment of Coupon Bonds as Interest Rates keep changing with the passage of time, which impacts the Yield to Maturity of such coupon-bearing Bonds. Since there are no interim cash flows, the investor is assured of a fixed rate of return. #3 - Longer Time frame
Zero Coupon Bond Calculator - What is the Market Price ... Benefits and Drawbacks of Zero Coupon Bonds. Zero coupon bonds have a duration equal to their time until maturity, unlike bonds which pay coupons. Duration of a bond is a length of time representing how sensitive a bond is to changes in interest rates. Since zero coupon bonds have an equal duration and maturity, interest rate changes have more ...
Risk-Neutral Pricing Formula for Zero-coupon bonds with ... I am looking for the equations or papers showing the risk-neutral pricing for zero-coupon bonds including default risk. I already tried Googling and searching SSRN and Jstor. bond zero-coupon risk-neutral. Share. Improve this question. Follow asked Apr 4, 2020 at 17:02. Jake Freeman Jake Freeman. 158 4 4 ...
› treasury-bills-vs-bondsTreasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) Bonds are debt instruments also issued by the government or corporate for tenure equal to or more than 2 years period. T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, they are issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value at the end of the tenure, which is the return on their investment.
Zero-Coupon Bonds: Pros and Cons Higher Yields: Firstly, zero-coupon bonds are perceived as higher-risk bonds. This is because investors pay money upfront and then do not have much control over it. Also, since the money is locked in over longer periods of time, the perceived risk is more.



/DurationandConvexitytoMeasureBondRisk2-0429456c85984ad3b220cd23a760cda5.png)





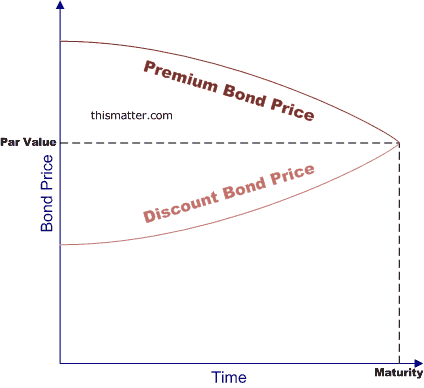
Post a Comment for "38 risk of zero coupon bonds"